Cyber threats in Australia seem to evolve every day, with a 39% increase in isolated compromises in FY2023-24 compared to the previous year, according to ACSC’s Annual Cyber Threat Report 2023-2024. While extensive compromises decreased slightly, low-level malicious attacks rose by 10%. Alarmingly, 30% of significant cyber incidents stemmed from exploiting public-facing applications, underscoring the importance of securing cloud environments.
Implementing a proactive and effective incident response strategy is no longer optional for organisations relying on AWS—it’s essential. Our experience demonstrates that most organisations do not have a security incident response plan, and even fewer have tested it! AWS Security Incident Response equips businesses with the tools, processes, and expertise to detect, contain, and recover from security incidents quickly and efficiently.
This article summarises the response procedures needed to combat threats and the role that AWS Security Incident Response experts play.
Cyber security incidents in Australia by severity category for FY 2023-24
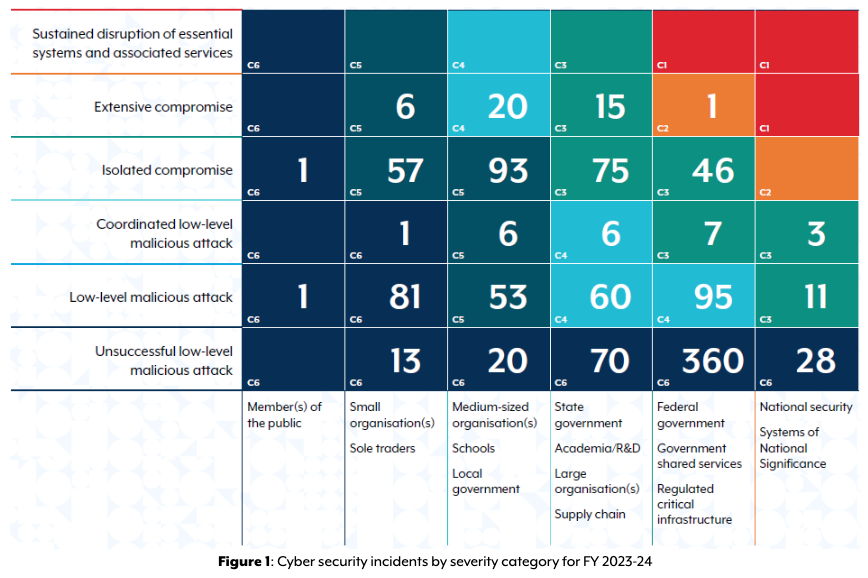
Source: ACSC
Understanding the AWS Shared Responsibility Model
While AWS provides powerful built-in security features, customers must actively secure their cloud environments. By understanding where AWS’s responsibility ends and where theirs begins, organisations can take full advantage of AWS’s security capabilities while ensuring their own workloads remain protected.
AWS Responsibilities: Security of the Cloud
AWS is responsible for the security of the cloud, meaning it protects the underlying infrastructure that powers cloud services. These responsibilities include:
- Physical Security of Data Centres: AWS protects its global network of data centres with multiple layers of security, including biometric access controls, 24/7 monitoring, and redundant power systems.
- Network Infrastructure: AWS manages the security of the networking components that connect customers to their cloud resources. It provides DDoS protection, encryption in transit, and network isolation tools to ensure customer data remains safe as it moves through AWS’s global infrastructure.
- Managed Services Security: AWS secures the core infrastructure of its managed services, including patching, operating system updates, and runtime security for services like Amazon S3, Amazon RDS, and AWS Lambda.
Customer Responsibilities: Security in the Cloud
Customers are responsible for how they use AWS services. We find that customers often think the platform or cloud provider covers all aspects of security. In fact, as a customer, you need to configure security settings, manage data protection, and control user access within your cloud environments. These responsibilities include:
- User Access Management: AWS provides Identity and Access Management (IAM) tools that allow customers to create fine-grained access controls. However, each organisation must configure IAM roles, enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA), and limit user privileges.
- Data Encryption and Protection: AWS offers encryption tools, such as AWS Key Management Service (KMS) and server-side encryption for S3, but customers must enable and manage these settings. Organisations that fail to encrypt sensitive data risk data breaches and non-compliance with industry regulations. Data protection is a shared responsibility—AWS provides encryption mechanisms, but customers decide how and when to implement them.
- Application Security and Configuration: While AWS secures the underlying infrastructure, customers must ensure their applications are designed and deployed securely. This includes patching vulnerabilities, configuring firewalls and securing APIs.
1. Proactive Threat Detection and Response
Identifying potential risks before they escalate can significantly reduce damage and ensure faster remediation. AWS provides a suite of tools to detect, analyse, and prioritise security threats across cloud environments, including AWS Config, Amazon GuardDuty and AWS Security Hub.
These tools reduce false positives and ensure security teams remain focused on actionable threats rather than sifting through excessive alerts. But while automation and AI-driven tools significantly improve threat detection and response times, human expertise remains critical in handling complex security incidents. AWS Security Incident Response experts provide:
- Comprehensive triage, analysis, and mitigation of critical security threats.
- Provide expert support for manual forensic investigations and fine-tuning automated playbooks.
- Reviewing and refining AI-detected anomalies, reducing false positives and providing accurate threat assessments.
2. Automating Incident Response Actions
Automation can reduce the response time for security incidents. AWS Security Incident Response experts rapidly detect, contain, and mitigate threats by combining their expertise with:
- Runbooks and Playbooks: Predefined automated workflows can manage common security incidents such as isolating compromised EC2 instances, revoking suspicious access keys, and rolling back unauthorised changes.
- AWS Lambda: Serverless functions that can automatically trigger remediation steps, such as disabling compromised IAM credentials or quarantining resources.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Using AWS CloudFormation, organisations can rebuild secure environments quickly following an incident, reducing downtime and ensuring security consistency.
Example Use Case:
For instance, an organisation facing an account compromise can have AWS Lambda automatically turn off affected credentials, block malicious IPs, and restore user permissions based on predefined playbooks—reducing downtime and limiting exposure.
3. Limiting the Damage with Containment and Recovery
Once a security threat is identified, rapid containment and recovery measures are critical to minimising damage. AWS Security Incident Response professionals play a crucial role in analysing security events, correlating data across multiple sources, and making quick decisions that automated tools alone cannot. Their role includes:
- Interpreting Security Signals: Automated tools can detect threats, but cybersecurity professionals must validate, investigate, and differentiate between real threats and false positives.
- Assessing Contextual Risks: Security events do not happen in isolation—analysts assess user behaviour, network activity, and access patterns to understand the full scope of an attack.
- Taking Immediate Action: Automated systems can apply default containment actions, but security teams must adapt their responses to unique attack scenarios and ensure that legitimate business functions are not unnecessarily disrupted.
- Identifying What Tools May Miss: Some threats, such as sophisticated insider attacks or zero-day exploits, may evade automated detection. Experienced cybersecurity professionals can spot anomalies that do not fit known attack patterns.
- IAM Access Control Adjustments: Security professionals review and refine automated IAM policies, ensuring that compromised accounts are locked down without disrupting business operations.
4. Post-Incident Analysis and Continuous Improvement
Post-incident recovery is not just about restoring data—it’s about ensuring the organisation is not vulnerable to the same attack again. Conducting thorough post-incident analysis ensures continuous improvement in security strategies. Cybersecurity experts:
- Conduct in-depth forensic analysis: Review incident logs to determine how the attack happened and whether any persistence mechanisms were left behind.
- Playbook Refinements: Update playbooks based on real-world attack patterns and adjust automated responses accordingly. This also includes identifying opportunities for automation.
Tracking Metrics: Evaluate response performance using:
- Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) – Time taken to identify a security threat.
- Mean Time to Recover (MTTR) – Time taken to restore normal operations.
- Time to Contain (TTC) – How quickly the organisation isolated a security event.
- Assess compliance impact: Coordinate legal or regulatory reporting if required.
Conclusion
AWS Security Incident Response equips an organisation with experience, processes, and tools that enable it to manage cloud security risks. AWS Security Incident Response Specialists offer an integrated approach, from proactive threat detection and automated response actions to thorough post-incident analysis. This enables enterprises to minimise downtime, reduce financial impacts and maintain their security posture.
RedBear Has the Specialist Touch to Help Minimise Your Incidents
As an AWS Security Incident Response Specialist, RedBear provides expert guidance, tailored workflows, and cutting-edge tools to help your organisation prepare for and respond to security incidents. Visit our Cloud Managed Security Services page to learn more about what we do.






